Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
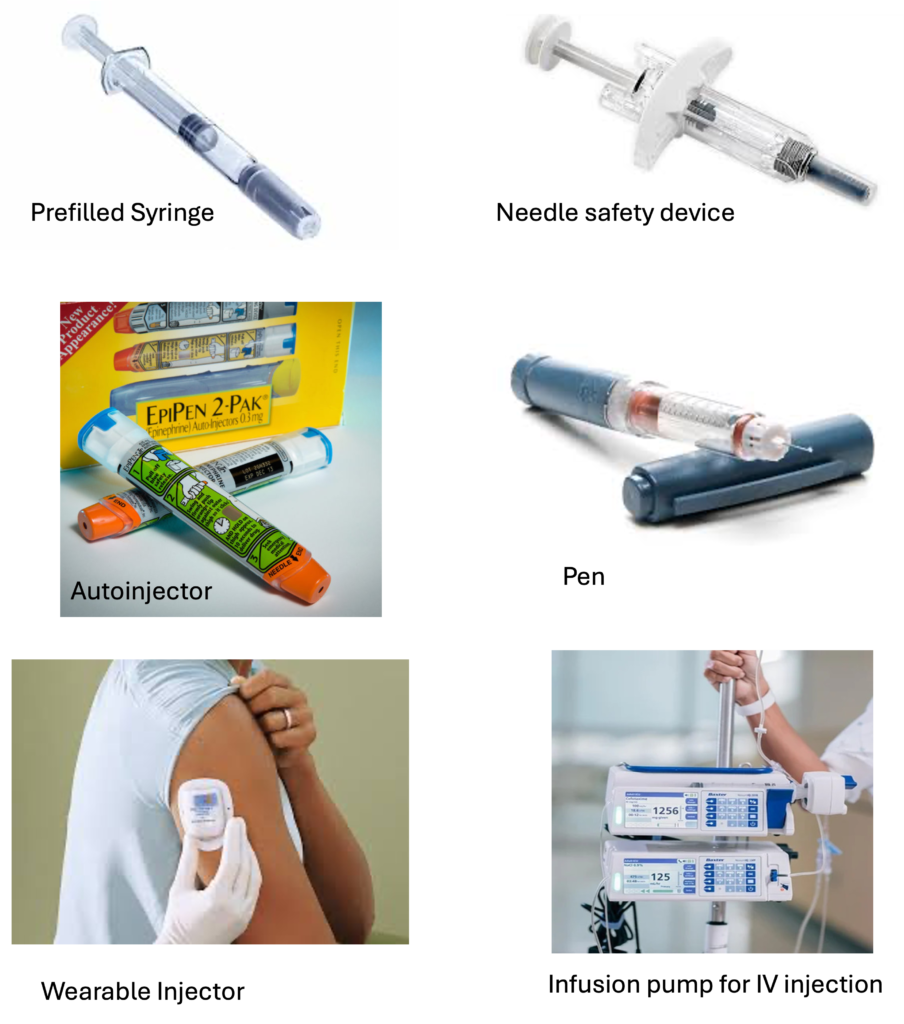
Wearable Injectors: These devices are worn on the body and can automatically administer drugs over time, useful for treatments that require multiple doses, like biologics.
Syringes: The most common and basic injectable device, often prefilled with medication. They can be manual or powered, and come in various sizes for different volumes.
Pens and Auto-Injectors: These are user-friendly devices designed for self-administration. They allow patients to inject drugs like insulin or biologics with ease and precision. Auto-injectors typically include a spring mechanism to automatically inject the medication after the device is positioned.
Microneedle Arrays: A newer form of injectable device that uses tiny needles to deliver drugs through the skin without causing significant pain or discomfort. These are being researched for vaccines and other biologics.
Infusion Pumps: These are electronic or mechanical devices designed for continuous or intermittent administration of medication, such as insulin pumps or pain pumps for chronic conditions.
Key benefits of injectable drug delivery devices include precise dosing, faster drug absorption compared to oral medications, and the ability to deliver large molecules (e.g., proteins, monoclonal antibodies) that would otherwise be degraded in the digestive system. However, challenges include the need for proper training, potential discomfort, and the risk of infections or injuries if not used correctly.
Overall, injectable drug delivery devices enhance patient compliance, particularly for chronic conditions requiring regular treatment, and are essential in modern medicine for various therapies.
Selecting the right combination products for biologics is a crucial step in ensuring that your biologic product achieves its intended therapeutic effect while meeting regulatory, safety, and market needs. Combination products typically consist of a biologic drug, a device (like an injector or pen), and sometimes a delivery system (e.g., a device for controlled release). The goal is to optimize patient experience, compliance, and clinical outcomes.
Here are key steps to help guide your decision-making process:
Key benefits of injectable drug delivery devices include precise dosing, faster drug absorption compared to oral medications, and the ability to deliver large molecules (e.g., proteins, monoclonal antibodies) that would otherwise be degraded in the digestive system. However, challenges include the need for proper training, potential discomfort, and the risk of infections or injuries if not used correctly.
Overall, injectable drug delivery devices enhance patient compliance, particularly for chronic conditions requiring regular treatment, and are essential in modern medicine for various therapies.
Selecting the right combination products for biologics is a crucial step in ensuring that your biologic product achieves its intended therapeutic effect while meeting regulatory, safety, and market needs. Combination products typically consist of a biologic drug, a device (like an injector or pen), and sometimes a delivery system (e.g., a device for controlled release). The goal is to optimize patient experience, compliance, and clinical outcomes.
Here are key steps to help guide your decision-making process:
Read more on combination products design & development, prefilled syringes, autoinjectors and wearables.